Myasthenia gravis (MG)
Lambert-Eaton syndrome
Autocephalus (AE)
Marginal lobe encephalitis (LE)
Optic neuromyelitis (NMO)
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
Guillain-barre syndrome (GBS)
Miller fisher syndrome
Polyneuropathy
Paraneoplastic syndrome (PNS)
Single-molecule array (Simoa) technology enables ultrasensitive protein detection that is suited to the development of peripheral blood-based assays for assessing neurological disorders. Simoa technology is based on the Quanterix Simoa HD-1 digital single molecular array analyzer, which can directly perform ultra-high sensitivity detection of biomarkers such as proteins and nucleic acids in serum and plasma. The advent of Simoa technology has changed the situation where neural markers could only be detected in cerebrospinal fluid in the past. At present, neurological biomarkers can be detected in peripheral blood using Simoa technology, thus changing the way of diagnosis of brain injury and neurodegenerative diseases. Simoa enables accurate quantitation of soluble immune signaling molecules in an unprecedented femtomolar range. In addition, Simoa technology has also greatly promoted the early detection of cancer, postoperative monitoring and precision medicine. Its main application areas include nerves, tumors, infectious diseases and immune inflammation. At present, there are hundreds of publications citing this technology in the world, including Nature, Science, Cell, Lancet, Nature Biotechnology, The Lancet Neurology, JAMA Neurology, etc.
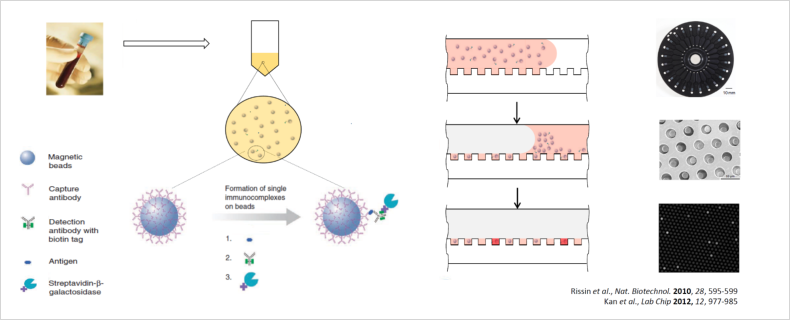
A high-level look at a Simoa Bead-based assay, from development to data analysis: (1) Paramagnetic particles coupled with antibodies designed to bind to specific targets are added to the sample. (2) Detection antibodies – capable of generating fluorescent product – are added. (3) The objective is to form an immunocomplex consisting of the bead, bound protein, and detection antibody. (4) At low concentrations, each bead will contain one bound protein, or none. (5) The sample is loaded into arrays, in the Simoa disc, consisting of more than 200,000 microwells – each large enough to hold one bead. (6) Enzymatic signal amplification with fluorescent substrate, fluorescence imaging and data reduction. (7) Data analysis – results can be viewed and analyzed on the board or exported to commonly used software packages or LIMS systems.
More than 1000 times more sensitive than ELISA
Ensure repeatability and accuracy of results
Detect multiple target molecules each time
Coefficient of variation (CVs) of the experimental results are usually less than 10%
Detection dynamic range more than 4 orders of magnitude
Using simple, well-established chemistry, researchers can explore significant unmet needs in life science research using digital biomarker analysis technology
| Biomarkers | Species | LoD (pg/ml) | Median (pg/ml) | Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDNF | Human | 0.011 | 11306 | C, E, S |
| Tau | Human | 0.019 | 1.65 | C, E, S |
| NF-light | Human | 0.038 | 5.33 | C, E, S |
| Aβ42 | Human | 0.044 | 4.7 | C, E |
| GFAP | Human | 0.211 | 88 | C, E, S |
| Aβ40 | Human | 0.522 | 65.97 | C, E |
| MMP-9 | Human | 0.581 | N/A | C, E, S |
| p-Tau231 | Human | 0.621 | N/A | C |
| pNF-heavy | Human | 0.663 | 30.82 | C, E, S |
| α-Synuclein | Human | 0.955 | 4145 | C, E, S |
| UCH-L1 | Human | 1.05 | 9.51 | C, E, S |
| NSE | Human | 1.296 | 7845 | C, E, S |
| TDP-43 | Human | 2.48 | N/A | C, E, S |
| Tau | Mouse | 0.615 | 26.7 | C, E, S |
C=CSF, E=EDTA plasma, S=serum
| Biomarkers | Species | LoD (pg/ml) | Median (pg/ml) | Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM-CSF | Human | 0.0019 | 0.0865 | E, S |
| IL13 | Human | 0.002 | 0.039 | E, S |
| IFN-α | Human | 0.0025 | 0.0036 | E, S |
| IL-15 | Human | 0.003 | 3.23 | E, S |
| IL-10 | Human | 0.0038 | 0.94 | E, S |
| IL-1α | Human | 0.004 | 0.0293 | E, S |
| IL-5 | Human | 0.004 | 0.22 | E, S |
| IL-17A | Human | 0.0042 | 0.124 | E, S |
| IL-4 | Human | 0.0046 | 0.024 | E, S |
| IL-12p70 | Human | 0.0048 | 1.95 | E, S |
| IL-22(Total) | Human | 0.0054 | 7.16 | E, S |
| IL-6 | Human | 0.0055 | 1.73 | E, S |
| TRAIL | Human | 0.0083 | 23.1 | E, S |
| IL36β | Human | 0.01 | 0.426 | E, S |
| IFN-γ | Human | 0.0104 | 0.333 | E, S |
| IL-2 | Human | 0.011 | 0.086 | E, S |
| C-Peptide | Human | 0.013 | 1559 | E, S |
| LIF | Human | 0.015 | 0.412 | E, S |
| IL-1β | Human | 0.016 | 0.058 | E, S |
| IL-12p40/IL-23 | Human | 0.02 | 51.3 | E, S |
| IL-28A | Human | 0.022 | 0.303 | E, S |
| TGFα | Human | 0.031 | 3.34 | E, S |
| MIP-1β | Human | 0.034 | 66.7 | E, S |
| CCL-11 | Human | 0.04 | N/A | E, S |
| IP-10 | Human | 0.052 | 105 | E, S |
| IL-8 | Human | 0.056 | 5.31 | E, S |
| IL-17C | Human | 0.065 | 1.66 | E, S |
| MCP-3 | Human | 0.124 | 0.445 | E, S |
| IL-23 | Human | 0.132 | 0.31 | E, S |
| HE4/WFDC2 | Human | 0.135 | 104 | E, S |
| TGF-β | Human | 0.137 | 0.31 | E, S |
| IL-3 | Human | 0.226 | 0.279 | E, S |
| IL33 | Human | 0.32 | 5.45 | E, S |
| CEA | Human | 0.486 | 1511.5 | E, S |
| MMP-9 | Human | 0.581 | N/A | E, S |
| Cathepsin S | Human | 0.7 | 6566 | E, S |
| Leptin | Mouse | 2.46 | 6083 | E, S |
| IL-1β | Mouse | 0.004 | 0.201 | E, S |
| IL-1α | Mouse | 0.0085 | 1.063 | E, S |
| IL17A/F | Mouse | 0.022 | 11.58 | E, S |
| GM-CSF | Mouse | 0.032 | N/A | E, S |
| IL-23 | Mouse | 0.033 | 4.89 | E, S |
| IL-6 | Mouse | 0.035 | 16 | E, S |
| IL-17A | Mouse | 0.088 | 33.76 | E, S |
| IL-22 | Mouse | 0.095 | 273.3 | E, S |
| IL-17F | Mouse | 0.102 | 11.01 | E, S |
| TGFα | Mouse | 0.132 | 22.6 | E, S |
C=CSF, E=EDTA plasma, S=serum